[ad_1]
Governments and private companies around the world are recognizing and working towards the potential of quantum computing, which could create “$450 billion to $850 billion in value over the next 15 to 30 years,” according to estimates in the Boston Consulting Group’s 2021 report. develop their own quantum strategies and research initiatives.
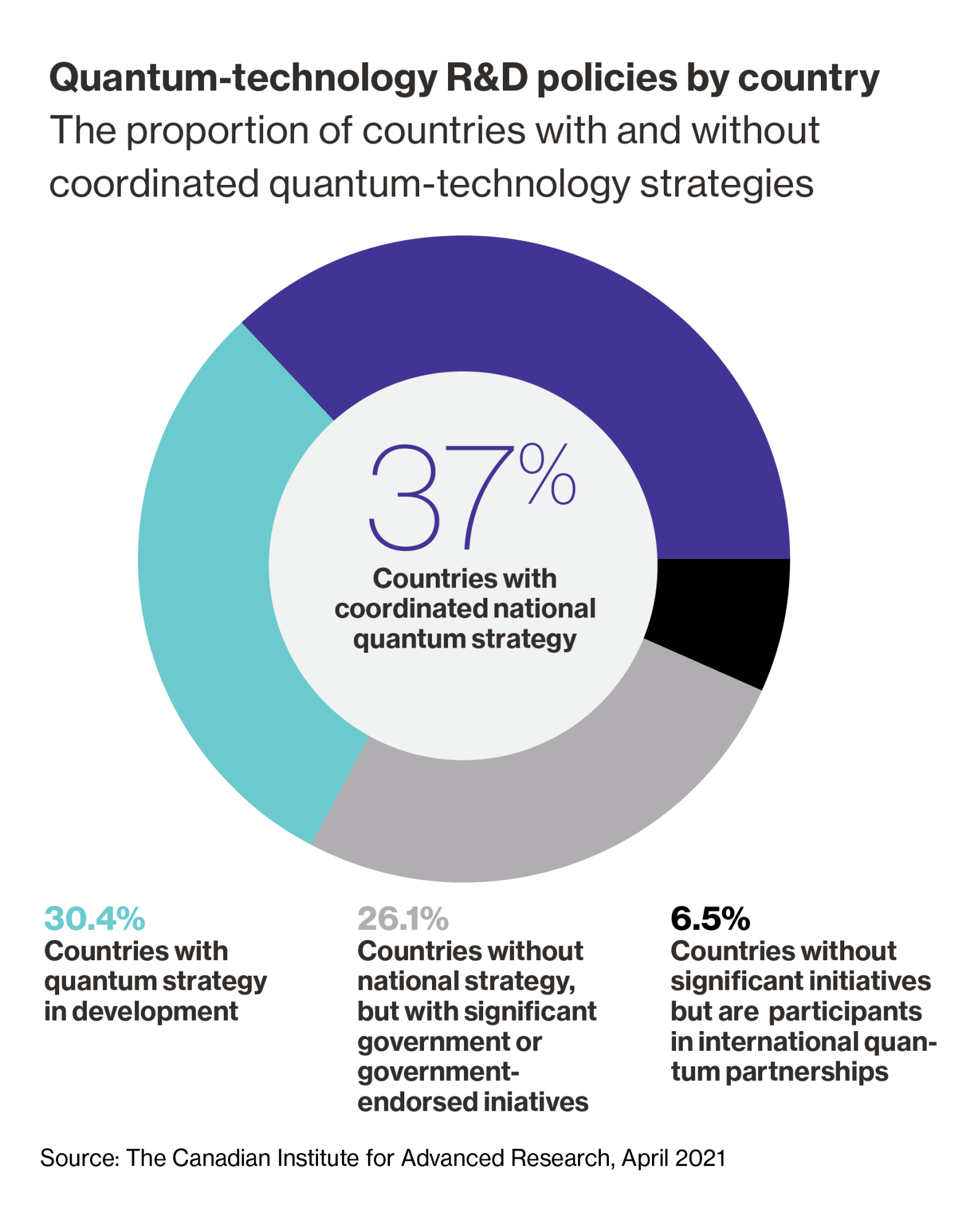
Preparing for the power of quantum
However, as quantum technology continues to advance, a dark cloud lurks on the horizon. Hackers may one day use this processing power to crack the public-key cryptosystems and other systems that underpin today’s secure interactions over the Internet, such as public key infrastructure, code signing systems, secure email and key. -Management systems. Experts warn that this is a major threat to modern digital security that needs to be addressed now. “This will completely break crypto systems,” says Dustin Moody, a mathematician at the US-based National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST).
While a full-scale quantum computer has yet to become a reality, the danger is imminent. Duncan Jones, head of cybersecurity at Quantenuum, a Cambridge and Colorado-based quantum computing company, says he’s concerned about one particular issue. “If I send you some encrypted data today and someone records it, they can get into it later,” Duncan says. “They don’t need a quantum computer to get into it today. They can just sit patiently at that data and then decrypt it in the future.”

To defend against such quantum attacks, post-quantum cryptography is emerging as an efficient and effective solution. It refers to a set of new encryption algorithms, especially public key algorithms, that can be implemented using today’s classical computers.
There is a growing urgency for governments and other organizations, as well as businesses of all sizes and in all industries to make their systems crypto agile and adopt such quantum resistant algorithms in their security frameworks. Companies and organizations cannot afford to wait and see how the quantum computing environment evolves. “Once quantum computers are built, the cost will skyrocket if they are adopted,” says Jung Hee Cheon, a professor of mathematics at Seoul National University in South Korea. Given the high risks, a proactive rather than reactive stance against such threats becomes crucial.
Download fully loaded report.
This content is produced by Insights, the exclusive content arm of MIT Technology Review. It was not written by the editorial staff of MIT Technology Review.
[ad_2]
Source link

